Large Tensorflow Datasets - My LibriSpeech Journey
Note: The purpose of this post is as a personal reflection and not as a tutorial
My recent project requires working with a great many audio files and Tensorflow datasets offers what looks to be a good mechanism for using them. I planned to use an established tensorflow dataset LibriSpeech as a model for my own, I didn’t expect however that it would be complicated to get working. This is my recount of trying to get the LibriSpeech dataset to work.
Issue 1: Download Speed Unworkably Slow
On my machine with mediocre internet it was estimated to take 12 hours to download. I proceeded to set up a Google Cloud Platform Virtual Machine which along with other advantages for machine learning projects, could download the dataset in less than an hour.
Issue 2: Using GCP DataFlow
This dataset is designed to be generated using parallel computation (https://www.tensorflow.org/datasets/beam_datasets), so I think the next step is to set up GCP DataFlow.
Learning Resources for DataFlow
I work through some guides to get a feel for DataFlow and Apache Beam
- https://console.cloud.google.com/dataflow/jobs?walkthrough_tutorial_id=dataflow_index
- https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/quickstarts
- https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/quickstarts/quickstart-python
Also useful to read Apache Beam Documentation
- https://beam.apache.org/documentation/sdks/python/
- https://beam.apache.org/documentation/programming-guide/
Uses Google Cloud Storage and gsutil
In order to understand what DataFlow is achieving, I researched the underpinning idea of MapReduce
Generating the LibriSpeech dataset using DataFlow
It is now time to use the above knowledge to generate the dataset. Like the dataflow tutorial example I execute all of these commands from the GCP console
Setting up the virtual machine
pip3 install --upgrade virtualenv \--user
python3 -m virtualenv env
source env/bin/activate
Installing Apache Beam and tensorflow-datasets
pip3 install apache-beam[gcp]
pip3 install tensorflow-datasets
Create Storage Bucket
gsutil mb gs://general-304503
Set parameters
DATASET_NAME=librispeech
DATASET_CONFIG=
GCP_PROJECT=general-304503
GCS_BUCKET=gs://general-304503
You will then need to create a file to tell Dataflow to install tfds on the workers
echo "tensorflow_datasets[$DATASET_NAME]" > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
Finally, you can launch the job using the command below
tfds build $DATASET_NAME \
--data_dir=$GCS_BUCKET/tensorflow_datasets \
--beam_pipeline_options=\
"runner=DataflowRunner,project=$GCP_PROJECT,job_name=$DATASET_NAME-gen,"\
"staging_location=$GCS_BUCKET/binaries,temp_location=$GCS_BUCKET/temp,"\
"requirements_file=/tmp/beam_requirements.txt"
Google Cloud Storage Buckets
However only a couple of minutes into the downloading the console crashes. I think this is because the GCP console is not designed for long running computations (like downloading a dataset). What this means is I will have to download the dataset to GCP bucket from a compute instance before executing the above commands.
According to the GCP compute engine documentation for mounting a bucket I have to install gcsfuse
Add the gcsfuse distribution URL as a package source and import its public key:
export GCSFUSE_REPO=gcsfuse-`lsb_release -c -s`
echo "deb http://packages.cloud.google.com/apt $GCSFUSE_REPO main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gcsfuse.list
curl https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Update the list of packages available and install gcsfuse
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gcsfuse
Mount the storage bucket
mkdir ~/general-304503
gcsfuse general-304503 ~/general-304503
After mounting I found that I could not interact with the files in the bucket. I needed to change the storage API permissions in the compute engine from Read Only to Full:
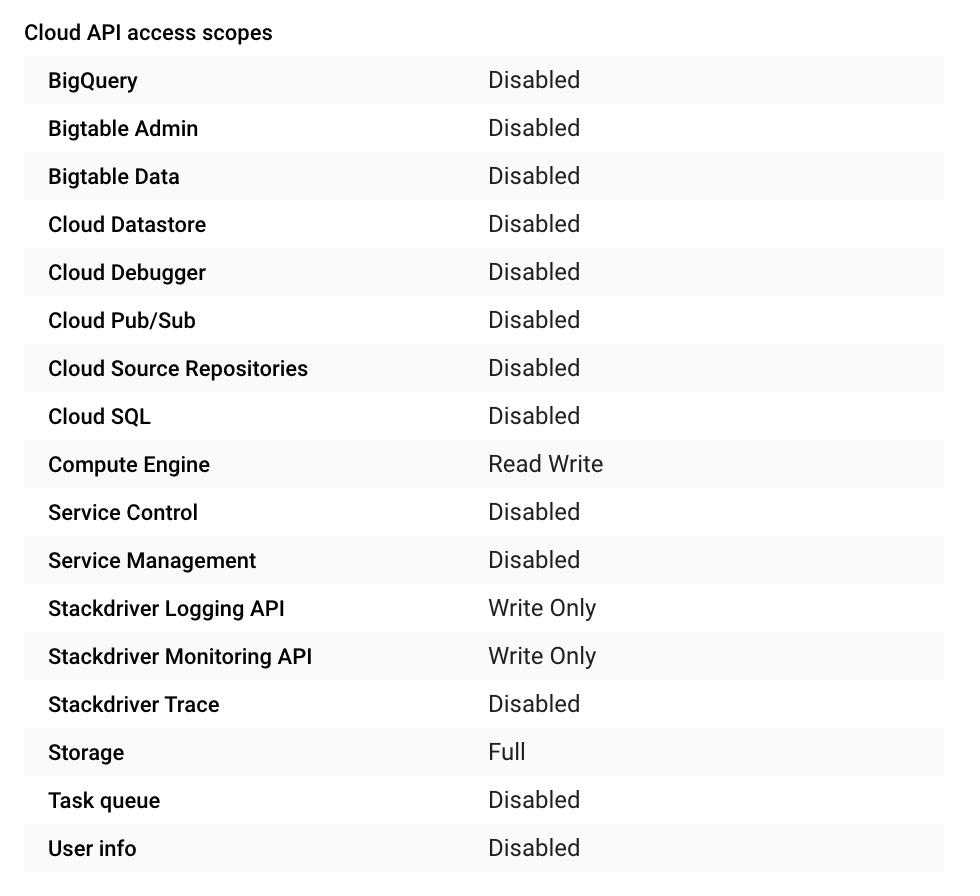
After getting the mounting to work I attempted to copy the downloaded dataset to the bucket however it was extremely slow (Estimated to take 48h). I think this is because the gcsfuse and probably just gcs buckets in general are not very efficient when it comes to many small files (After extraction there are almost 300,000 files). I looked briefly into using disks with DataFlow but I am not sure how to mount the same disk to different workers and in fact the documentation seems to suggest this is not possible.
Persistent disk resources The Dataflow service is currently limited to 15 persistent disks per worker instance when running a streaming job. Each persistent disk is local to an individual Compute Engine virtual machine. Your job may not have more workers than persistent disks; a 1:1 ratio between workers and disks is the minimum resource allotment.
Instead I am going to see what I can do to optimise gcsfuse.
Using gsutil to upload to a bucket
In my research to see if there was some option for more efficient upload in gcsfuse, I realised that I could perform the task with gsutil cp.
I copy the code from the documentation given here: https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/gsutil/commands/cp.
Use the -r option to copy an entire directory tree. For example, to upload the directory tree dir:
gsutil cp -r dir gs://my-bucket
If you have a large number of files to transfer, you can perform a parallel multi-threaded/multi-processing copy using the top-level gsutil -m option (see gsutil help options):
gsutil -m cp -r dir gs://my-bucket
I executed the second command to upload the downloaded dataset from the disk to the bucket and it took about 20m so this is much better.
Peforming the generation on DataFlow
I first tried imitating the DataFlow tutorial where all commands were executed from the console but I found that I could not install tensorflow-datasets there. I discovered that the DataFlow tutorial can actually also be exectuted from a virtual machine with API permissions so going forward thats what I am using.
My first attempt yielded this exception:
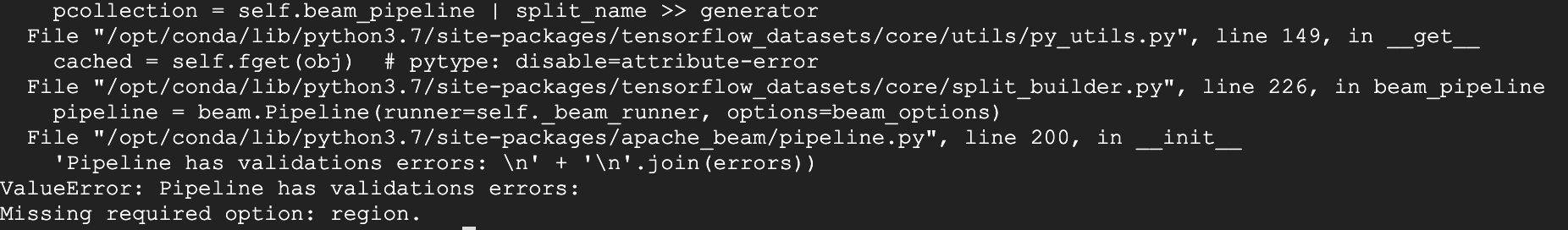
I realised that this meant that I needed to define a region for the DataFlow execution. This wasn’t in the pipeline options in the tensorflow apache guide but was in the dataflow tutorial.
Here is the change that needs to be made to the tfds build command to define the region:
tfds build $DATASET_NAME \
--data_dir=$GCS_BUCKET/tensorflow_datasets \
--beam_pipeline_options=\
"runner=DataflowRunner,project=$GCP_PROJECT,job_name=$DATASET_NAME-gen,"\
"staging_location=$GCS_BUCKET/binaries,temp_location=$GCS_BUCKET/temp,"\
"requirements_file=/tmp/beam_requirements.txt,region=us-central1"
Finally it is about to create the job on GCP, however about 16m into the execution there is an exception. Here is the graph where the blocks that failed are visible:
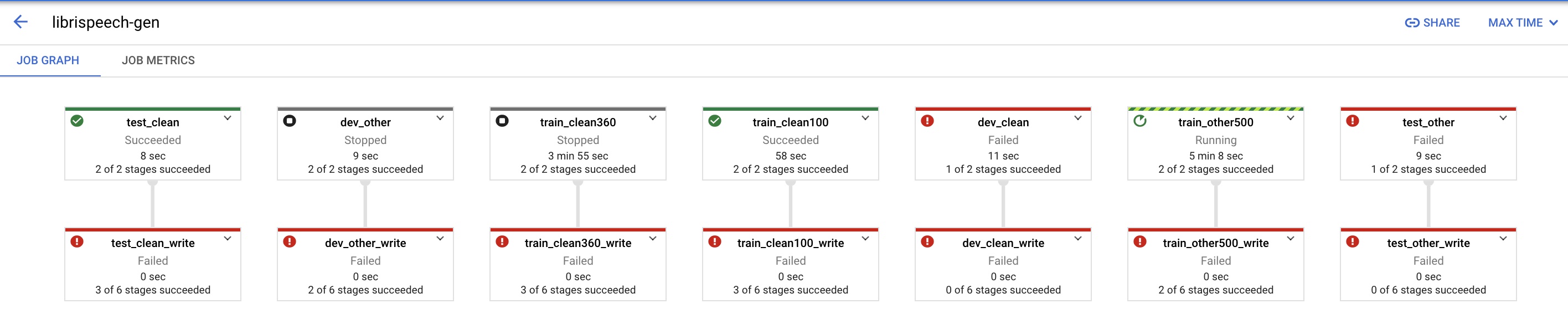
This is the exception that occured:

Before I start trying to debug this, I will check if installing tfds-nightly instead of tensorflow-datasets will fix the problem. That will involve executing these commands:
pip3 uninstall tensorflow-datasets
pip3 install tfds-nightly
echo "tfds-nightly[$DATASET_NAME]" > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
I however get this error:
ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement tfds-nightly[librispeech]
What I am going to try is installing the entirety of tfds-nightly on the workers.
echo "tfds-nightly" > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
Still returns errors. I think what is happening is that the tfds command is not updated when I uninstall tensorflow-datasets and install tfds-nightly. So I need to look at doing this without the tfds command.
I found instructions to do this in the ReadMe for Google Research text-to-text transfer transformer.
pip install tfds-nightly[c4]
echo 'tfds-nightly[c4]' > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
python -m tensorflow_datasets.scripts.download_and_prepare \
--datasets=c4/en \
--data_dir=gs://$MY_BUCKET/tensorflow_datasets \
--beam_pipeline_options="project=$MY_PROJECT,job_name=c4,staging_location=gs://$MY_BUCKET/binaries,temp_location=gs://$MY_BUCKET/temp,runner=DataflowRunner,requirements_file=/tmp/beam_requirements.txt,experiments=shuffle_mode=service,region=$MY_REGION"
They used a different dataset but it can be modified to fit my use.
pip3 install tfds-nightly[$DATASET_NAME]
echo "tfds-nightly[$DATASET_NAME]" > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
python -m tensorflow_datasets.scripts.download_and_prepare \
--datasets=$DATASET_NAME \
--data_dir=$GCS_BUCKET/tensorflow_datasets \
--beam_pipeline_options="project=$GCP_PROJECT,job_name=test2,staging_location=$GCS_BUCKET/binaries,temp_location=$GCS_BUCKET/temp,runner=DataflowRunner,requirements_file=/tmp/beam_requirements.txt,region=us-central1"
It is still failing. I now think that is is the actual installation of tfds-nightly on the workers that is failing. This is what it is trying to execute.
INFO[stager.py]: Executing command: ['/home/jsjsrobert500/env/bin/python', '-m', 'pip', 'download', '--dest', '/tmp/dataflow-requirements-cache', '-r', '/tmp/beam_requirements.txt', '--exists-action', 'i', '--no-bin
ary', ':all:']
I test the corresponding command in a terminal.
echo "tfds-nightly[$DATASET_NAME]" > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
/home/jsjsrobert500/env/bin/python -m pip download --dest /tmp/dataflow-requirements-cache -r /tmp/beam_requirements.txt --exists-action i --no-binary :all:
If the beam requirements is tensorflow-datasets there is not problem but with the nightly we get these errors:
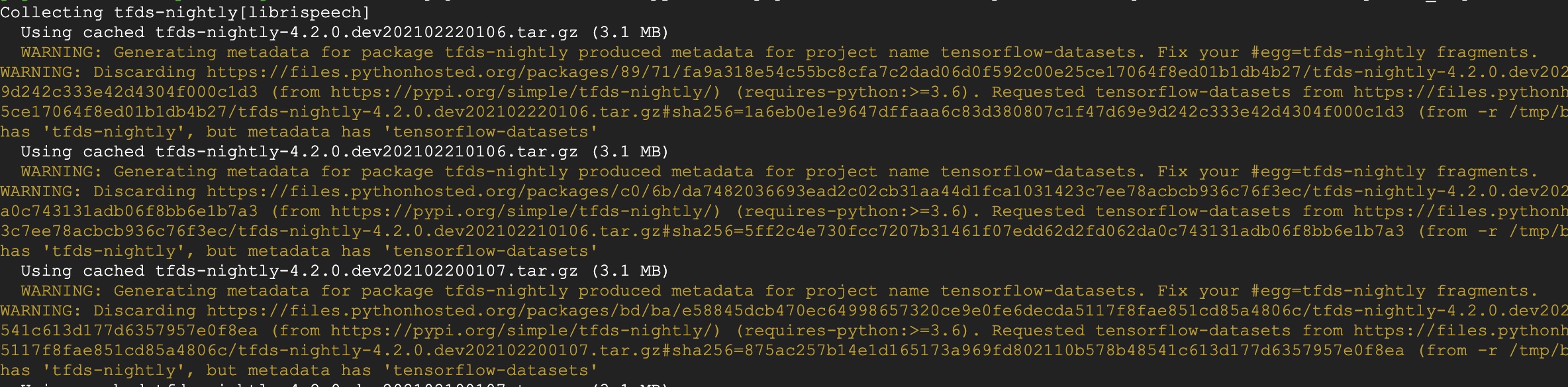
Now it is easier to see what is happening. Clearly pip is iterating through the nightly releases and rejecting each of them for some reason. Here is a full printout of one of the warnings:
Using cached tfds-nightly-4.2.0.dev202102220106.tar.gz (3.1 MB)
WARNING: Generating metadata for package tfds-nightly produced metadata for project name tensorflow-datasets. Fix your #egg=tfds-nightly fragments.
WARNING: Discarding https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/89/71/fa9a318e54c55bc8cfa7c2dad06d0f592c00e25ce17064f8ed01b1db4b27/tfds-nightly-4.2.0.dev202102220106.tar.gz#sha256=1a6eb0e1e9647dffaaa6c83d380807c1f47d69e
9d242c333e42d4304f000c1d3 (from https://pypi.org/simple/tfds-nightly/) (requires-python:>=3.6). Requested tensorflow-datasets from https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/89/71/fa9a318e54c55bc8cfa7c2dad06d0f592c00e2
5ce17064f8ed01b1db4b27/tfds-nightly-4.2.0.dev202102220106.tar.gz#sha256=1a6eb0e1e9647dffaaa6c83d380807c1f47d69e9d242c333e42d4304f000c1d3 (from -r /tmp/beam_requirements.txt (line 1)) has inconsistent name: filename
has 'tfds-nightly', but metadata has 'tensorflow-datasets'
I found a github issue where someone mentioned a similar problem involving metadata. One of the suggested solutions was downgrading pip to a version lower than 20.
/home/jsjsrobert500/env/bin/python -m pip install pip==19.0.1
After doing this pip no longer rejects all of the nightly packages.
However the problem where the DataFlow job crashes after about 15m is still present.
Issue 3: The generation code had a bug
There was a bug in librispeech.py that prevented generation. When running on dataflow it is difficult to see the reason but by executing this python code on a single machine it is easy to see where the problem is.
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
ds = tfds.load('librispeech', split='train_clean100', shuffle_files=True, data_dir='./')
I forked the tensorflow datasets repository on github and found the location of exception, it was a one line fix in tensorflow_datasets/audio/librispeech.py.
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(path, transcript_file)) as f:
changed to:
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(transcript_file) as f:
I actually found an issue on github where someone had made the exact same change as me but their pull request had many other unrelated changes so no one had reviewed it.
Issue 4: Installing on DataFlow Workers
Having made the fix on my github, I had some difficultly installing it on the dataflow workers. I also realised that I needed to install other non-python dependencies such as ffmpeg
After making the change on my fork of tensorflow datasets. I put the clone command I usually use to install packages from git in the requirements:
echo "git+https://github.com/Jaidon-Smith/datasets.git" > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
However after running this and checking the logs I realised that the workers can not use git to install so I will have to explore another way of allowing them to obtain the package.
This post gives instructions for installing from a tarball so that git does not have to be installed.
Installing via tarballs
An alternative that avoids Git is to install from a tarball URL, that the major hosted Git solutions provide, for example:
# GitHub
python -m pip install https://github.com/django/django/archive/45dfb3641aa4d9828a7c5448d11aa67c7cbd7966.tar.gz
# GitLab
python -m pip install https://gitlab.com/pycqa/flake8/-/archive/3.7.7/flake8-3.7.7.tar.gz
# Bitbucket
python -m pip install https://bitbucket.org/hpk42/tox/get/2.3.1.tar.gz
I looked into creating these tarballs but then I found that github automatically creates them. Here is the pip command to install from the tarball.
python -m pip install --upgrade https://github.com/Jaidon-Smith/datasets/archive/master.tar.gz
Here is the corresponding command to create the requirements.
echo "https://github.com/Jaidon-Smith/datasets/archive/master.tar.gz" > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
I execute the dataflow again, it crashes because I had not installed pydub. I update the requirements to install pydub.
echo "https://github.com/Jaidon-Smith/datasets/archive/master.tar.gz" > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
echo "pydub" >> /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
I try again, it crashes with this error:
RuntimeError: FileNotFoundError: Error for gs://general-304503/tensorflow_datasets/downloads/extracted/TAR_GZ.openslr.org_resources_12_dev-otherEmYcSOjD_h3iwcqkw-E1GTv7GBFYTxH1ad0SZFqoQ2U.tar.gz/LibriSpeech/dev-othe
r/6123/59186/6123-59186-0023.flac: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'ffprobe': 'ffprobe'
A quick search suggests that the solution may be to install ffprobe, so I update my requirements:
echo "https://github.com/Jaidon-Smith/datasets/archive/master.tar.gz" > /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
echo "pydub" >> /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
echo "ffprobe" >> /tmp/beam_requirements.txt
No this did not fix it. I think the problem is that ffmpeg needs to be installed on the workers. I need to follow the instructions here to include a setup.py:
I create a setup.py file with commands to install ffmpeg:
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
"""Setup.py module for the workflow's worker utilities.
All the workflow related code is gathered in a package that will be built as a
source distribution, staged in the staging area for the workflow being run and
then installed in the workers when they start running.
This behavior is triggered by specifying the --setup_file command line option
when running the workflow for remote execution.
"""
from distutils.command.build import build as _build
import subprocess
import setuptools
# This class handles the pip install mechanism.
class build(_build): # pylint: disable=invalid-name
"""A build command class that will be invoked during package install.
The package built using the current setup.py will be staged and later
installed in the worker using `pip install package'. This class will be
instantiated during install for this specific scenario and will trigger
running the custom commands specified.
"""
sub_commands = _build.sub_commands + [('CustomCommands', None)]
# Some custom command to run during setup. The command is not essential for this
# workflow. It is used here as an example. Each command will spawn a child
# process. Typically, these commands will include steps to install non-Python
# packages. For instance, to install a C++-based library libjpeg62 the following
# two commands will have to be added:
#
# ['apt-get', 'update'],
# ['apt-get', '--assume-yes', install', 'libjpeg62'],
#
# First, note that there is no need to use the sudo command because the setup
# script runs with appropriate access.
# Second, if apt-get tool is used then the first command needs to be 'apt-get
# update' so the tool refreshes itself and initializes links to download
# repositories. Without this initial step the other apt-get install commands
# will fail with package not found errors. Note also --assume-yes option which
# shortcuts the interactive confirmation.
#
# The output of custom commands (including failures) will be logged in the
# worker-startup log.
CUSTOM_COMMANDS = [
['apt-get', 'update'],
['apt-get', '--assume-yes', 'install', 'ffmpeg'],
]
class CustomCommands(setuptools.Command):
"""A setuptools Command class able to run arbitrary commands."""
def initialize_options(self):
pass
def finalize_options(self):
pass
def RunCustomCommand(self, command_list):
print('Running command: %s' % command_list)
p = subprocess.Popen(
command_list,
stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT)
# Can use communicate(input='y\n'.encode()) if the command run requires
# some confirmation.
stdout_data, _ = p.communicate()
print('Command output: %s' % stdout_data)
if p.returncode != 0:
raise RuntimeError(
'Command %s failed: exit code: %s' % (command_list, p.returncode))
def run(self):
for command in CUSTOM_COMMANDS:
self.RunCustomCommand(command)
setuptools.setup(
name='dummyname',
version='0.0.1',
description='Monthly landsat workflow package.',
install_requires=[],
packages=setuptools.find_packages(),
py_modules=[],
cmdclass={
# Command class instantiated and run during pip install scenarios.
'build': build,
'CustomCommands': CustomCommands,
}
)
I also modify the command to start the dataflow job to include the setup.py.
python -m tensorflow_datasets.scripts.download_and_prepare \
--datasets=$DATASET_NAME \
--data_dir=$GCS_BUCKET/tensorflow_datasets \
--beam_pipeline_options="project=$GCP_PROJECT,job_name=test9,staging_location=$GCS_BUCKET/binaries,temp_location=$GCS_BUCKET/temp,runner=DataflowRunner,requirements_file=/tmp/beam_requirements.txt,region=us-central1,num_workers=5,setup_file=/tmp/setup.py"
Conclusion
Finally it looks like the dataflow job would succeed. I won’t run it to completion because it takes a long time but I tested on a modified version that contains a subset of the data and it terminated successfully.
